Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two people who are currently out of work. Tim is not looking for work because there have been many job cuts where he lives, and he doesn't think it likely that he will find work. Bev is not currently looking for work, but she would like a job, and she has looked for work in the past. The Bureau of Labor Statistics considers
A) both Tim and Bev to be marginally attached workers.
B) neither Tim nor Bev to be marginally attached workers.
C) only Tim to be a marginally attached worker.
D) only Bev to be a marginally attached worker.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Not all unemployment ends with the job seeker finding a job.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some persons are counted as out of the labor force because they have made no serious or recent effort to look for work. However, some of these individuals may want to work even though they are too discouraged to make a serious effort to look for work. If these individuals were counted as unemployed instead of out of the labor force, then
A) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be higher.
B) the unemployment rate would be higher ,and the labor-force participation rate would be lower.
C) the unemployment rate would be lower, and the labor-force participation rate would be higher.
D) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be lower.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unemployment generated by the existence of labor unions is structural unemployment and so contributes to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the minimum wage
A) increases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
B) decreases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
C) increases the quantity of labor demanded but decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
D) decreases the quantity of labor demanded but increases the quantity of labor supplied.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sirius has just finished high school and started looking for his first job, but has not yet found one. Other things the same, the unemployment rate
A) and the labor-force participation rate both increase.
B) increases, and the labor-force participation rate is unaffected.
C) is unaffected, and the labor-force participation rate increases.
D) and the labor-force participation rate are both unaffected.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of right-to-work laws, workers
A) that went on strike could be permanently replaced.
B) might be required to join the union if they worked for a unionized firm.
C) would not be able to unionize.
D) would not be able to strike.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Someone who loses his job at a truck factory because the demand for trucks has fallen and the demand for cars has risen, is structurally unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the adult population is 6 million, the number of employed is 3.8 million, and the labor-force participation rate is 70%. What is the unemployment rate?
A) 6.7%
B) 9.5%
C) 10.5%
D) 28%
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sectoral changes in demand
A) create frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates creates structural unemployment.
B) create structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates creates frictional unemployment.
C) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates both create structural unemployment.
D) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates both create frictional unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions contribute to
A) structural unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment but not structural unemployment.
C) both structural unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) neither structural unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs, then there would be no
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) natural rate of unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Fulltime students and homemakers are included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "unemployed" category.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More than one-third of the unemployed are recent entrants into the labor force.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Within the U.S. population, women of prime working age (ages 25-54) have higher rates of unemployment than men of prime working age (ages 25-54), regardless of race.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-4
2010 Labor Data for Adults (ages 16 and older) in Meditor 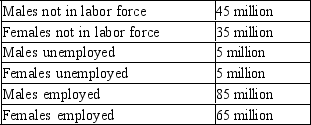 -Refer to Table 28-4. What is the adult labor force in Meditor?
-Refer to Table 28-4. What is the adult labor force in Meditor?
A) 90 million
B) 150 million
C) 160 million
D) 230 million
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Efficiency wages contribute to
A) frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C) structural unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) structural unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that some country had an adult population of about 50 million, a labor-force participation rate of 60 percent, and an unemployment rate of 5 percent. How many people were unemployed?
A) 1.425 million
B) 1.5 million
C) 2.5 million
D) 5 million
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-7
Below is data about the labor market in the city of Productionville. 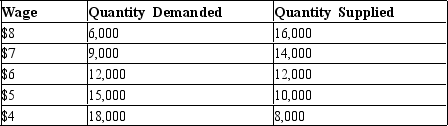 -Refer to Table 28-7. If the local government imposed a minimum wage of $6 in Productionville, how many people would be unemployed?
-Refer to Table 28-7. If the local government imposed a minimum wage of $6 in Productionville, how many people would be unemployed?
A) 0
B) 2,000
C) 3,000
D) 5,000
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 401 - 420 of 678
Related Exams