A) interest rate and investment to rise.
B) interest rate and investment to fall.
C) interest rate to rise and investment to fall.
D) interest rate to fall and investment to rise.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A significant lag for monetary policy is the time it takes to for a change in the money supply to change the economy. A significant lag for fiscal policy is the time it takes to pass legislation authorizing it.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which U.S. president, when asked why he had proposed a tax cut, responded by saying "To stimulate the economy. Don't you remember your Economics 101?"
A) Dwight D. Eisenhower
B) John F. Kennedy
C) Ronald Reagan
D) Bill Clinton
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If expected inflation is constant, then when the nominal interest rate increases, the real interest rate
A) increases by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
B) increases by the change in the nominal interest rate.
C) decreases by the change in the nominal interest rate.
D) decreases by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A) The price level rises.
B) The price level falls.
C) The Fed purchases government bonds on the open market.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Stock prices often rise when the Fed raises interest rates.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reduction in personal income taxes increases Aggregate Demand through
A) an increase in investment spending.
B) an increase in national savings.
C) an increase in private savings.
D) an increase in personal consumption.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in government spending initially and primarily shifts
A) aggregate demand to the right.
B) aggregate demand to the left.
C) aggregate supply to the right.
D) neither aggregate demand nor aggregate supply in either direction.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity preference theory, an increase in the overall price level of 10 percent
A) increases the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn decreases the quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) decreases the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn increases the quantity of goods and services demanded.
C) increases the quantity of money supplied by 10 percent, leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged.
D) decreases the quantity of money demanded by 10 percent, leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following policy alternatives would be an appropriate response to a sharp increase in investment spending, assuming policymakers want to stabilize output?
A) increase taxes
B) increase the money supply
C) increase government expenditures
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Other things equal, the higher the price level, the higher is the real wealth of households.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to their impact on aggregate demand for the U.S. economy, which of the following represents the correct ordering of the wealth effect, interest-rate effect, and exchange-rate effect from most important to least important?
A) wealth effect, exchange-rate effect, interest-rate effect
B) exchange-rate effect, interest-rate effect, wealth effect
C) interest-rate effect, wealth effect, exchange-rate effect
D) interest-rate effect, exchange-rate effect, wealth effect
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the interest rate falls,
A) the quantity of money demanded falls, which would reduce a shortage.
B) the quantity of money demanded falls, which would reduce a surplus.
C) the quantity of money demanded rises, which would reduce a shortage.
D) the quantity of money demanded rises, which would reduce a surplus.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, then initially there is a
A) shortage in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
B) shortage in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
C) surplus in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
D) surplus in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in the interest rate bring the money market into equilibrium according to
A) both liquidity preference theory and classical theory.
B) neither liquidity preference theory nor classical theory.
C) liquidity preference theory, but not classical theory.
D) classical theory, but not liquidity preference theory.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 34-14 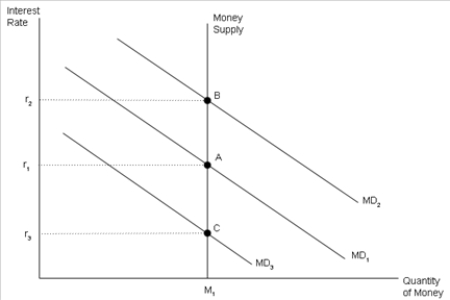 -Refer to Figure 34-14. Households' desired money holdings are given by MD1. If the current rate of interest is r3, then there is excess _____. Households will _____ interest-earning assets, which causes the interest rate to _____.
-Refer to Figure 34-14. Households' desired money holdings are given by MD1. If the current rate of interest is r3, then there is excess _____. Households will _____ interest-earning assets, which causes the interest rate to _____.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 34-2. The following facts apply to a small, imaginary economy. • Consumption spending is $6,720 when income is $8,000. • Consumption spending is $7,040 when income is $8,500. -Refer to Scenario 34-2. The multiplier for this economy is
A) 1.31.
B) 6.25.
C) 2.78.
D) 2.27.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Supply-side economists believe that a reduction in the tax rate
A) always decrease government tax revenue.
B) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) provides no incentive for people to work more.
D) would decrease consumption.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run, open-market sales
A) increase the price level and real GDP.
B) decrease the price level and real GDP.
C) increases the price level and decreases real GDP.
D) decreases the price level and increases real GDP.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose households attempt to increase their money holdings. To stabilize output by countering this increase in money demand, the Federal Reserve would
A) increase government spending.
B) increase the money supply.
C) decrease government spending.
D) decrease the money supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 510
Related Exams