A) First, choose between A and B. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and D.
B) First, choose between B and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and C. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and b.
C) First, choose between C and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and A. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and c.
D) First, choose between C and D. Second, voters choose between the winner of the first vote and B. Third, voters choose between the winner of the second vote and A.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in a Borda count election, outcome X is preferred to outcome Y, and outcome Y is preferred to outcome Z, when outcomes X, Y, and Z are all available options. When Y is removed as an option, however, outcome Z is preferred to outcome X. This would violate Arrow's assumption that voting systems should satisfy
A) unanimity.
B) transitivity.
C) the independence of irrelevant alternatives.
D) no dictators.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a corporation decides to include its own corporate stock as part of the compensation for its employees, it is trying to solve the
A) adverse selection problem.
B) principal-agent problem.
C) lemons problem.
D) signaling problem.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You own an ice cream store and are concerned that an employee may be giving generous scoops to friends and relatives and smaller scoops to some other customers. This may be reducing sales. If you want your employee to stop giving larger scoops to friends and relatives, which of the following is not a good approach?
A) Make visits to the store at the same time each day.
B) Pay employees an above equilibrium wage.
C) Give your employees a monthly bonus based on profits.
D) None of the above are good approaches.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Borda count is a voting method often used in polls that rank sports teams.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mankiw argues that a primary difference between taxing products like gasoline and taxing soda and other sugary drinks is that
A) consumption of gasoline causes negative externalities on society while consumption of soda affects the consumer.
B) the government can generate significant revenue from the gas tax but not from a soda tax.
C) gasoline has inelastic demand but soda has elastic demand.
D) Both a and c are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-13
A high school Spanish class and their teacher are planning to take a Spring Break trip abroad but they have to decide where to go. They have narrowed the options to: Spain, Mexico, Ecuador, and Costa Rica. The voters' preferences are shown in the table below.
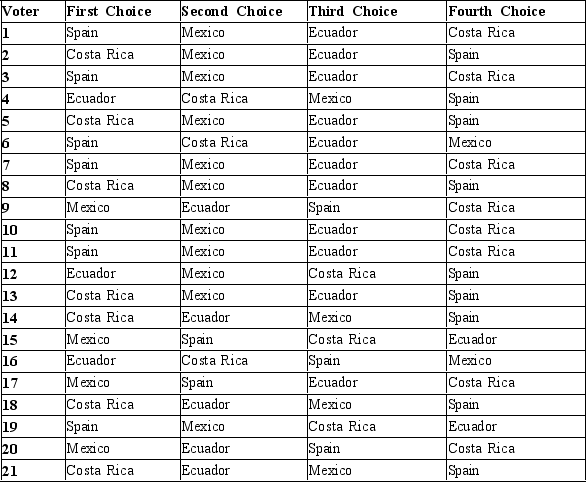 -Refer to Table 22-13. In a pairwise election between Costa Rica and Ecuador and then a second election between the winner and Mexico, which countries are chosen?
-Refer to Table 22-13. In a pairwise election between Costa Rica and Ecuador and then a second election between the winner and Mexico, which countries are chosen?
A) Costa Rica is chosen in the in the first and second elections.
B) Costa Rica is chosen in the first election and Mexico is chosen in the second.
C) Ecuador is chosen in the first and second elections.
D) Ecuador is chosen in the first election and Mexico is chosen in the second.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Rather than always choosing the best course of action, humans make decisions that are merely good enough. In other words, they are
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In corporations, a principal-agent problem can arise when
A) the shareholders are the principal and the managers are the agent.
B) the board of directors is the principal and the managers are the agent.
C) the shareholders are the principal and the board of directors is the agent.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-3 At issue in a particular city vote is how much to spend, per person, on road repair next year. Among the 10,000 voters, 2,900 prefer to spend $500 per person, but no more; 2,200 prefer to spend $600 per person, but no more; 1,900 prefer to spend $800 per person, but no more; 1,600 prefer to spend $1,200 but no more, and 1,400 prefer to spend $1,400 per person, but no more. -Refer to Scenario 22-3. If there is a vote on whether to spend $800 per person or $1,200 per person, the median voter will vote to spend
A) $800 per person and the voting outcome will be $800 per person.
B) $800 per person and the voting outcome will be $1200 per person.
C) $1200 per person and the voting outcome will be $800 per person.
D) $1200 per person and the voting outcome will be $1200 per person.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Information asymmetry refers to
A) the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage in dishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior.
B) the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to become undesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party.
C) an action taken by an informed party to reveal private information to an uninformed party.
D) a difference in access to relevant knowledge.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to behavioral economics, participants in a half-marathon are likely to have trained
A) more than they planned and run faster than they anticipated.
B) more than they planned but run slower than they anticipated.
C) less than they planned and run slower than they anticipated.
D) less than they planned but run faster than they anticipated.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People with hidden health problems are more likely to buy health insurance than are other people. This is an example of
A) moral hazard and makes the cost of health insurance higher than otherwise.
B) moral hazard and makes the cost of health insurance lower than otherwise.
C) adverse selection and makes the cost of health insurance higher than otherwise.
D) adverse selection and makes the cost of health insurance lower than otherwise.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-18
The following table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible alternatives as well as the percentage of the electorate with the given preferences.
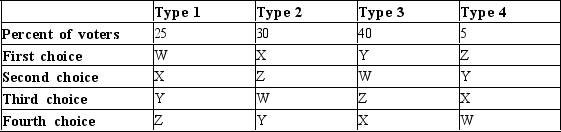 -Refer to Table 22-18. In a majority vote between alternatives X and Y, what percentage of the votes would X receive?
-Refer to Table 22-18. In a majority vote between alternatives X and Y, what percentage of the votes would X receive?
A) 35%
B) 45%
C) 55%
D) 65%
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adverse selection
A) occurs when the overall quality of choices facing a consumer is very low.
B) is a greater problem for employees than employers.
C) occurs more frequently in the market for new cars than used cars.
D) is not easily remedied by free markets.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet paradox shows that
A) allocations of resources based on majority rule are always inefficient.
B) problems in counting votes can negate legitimate democratic outcomes.
C) the order on which things are voted can affect the result.
D) transitive preferences are inconsistent with rationality.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Moral hazard occurs when
A) an employer closely monitors an employee.
B) two people consider a trade with each other and one person has relevant information about some aspect of the product's quality that the other person lacks.
C) an employee lacks an incentive to promote the best interests of the employer, and the employer cannot observe the actions of the employee.
D) an employee closely monitors the actions of her employer.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A travel agency offers a money-back guarantee for vacationers taking their first cruise in case they do not enjoy the experience. This guarantee is an example of
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Susan buys automobile insurance from Provident Insurance Company. If Susan avoids having an accident for three years, Provident will reduce the premiums she has to pay for her insurance. Nevertheless, she routinely drives while eating or texting and speeds up to try to make it through yellow lights.
A) This is an adverse selection problem which should be corrected with government intervention.
B) Susan is a principal and Provident is an agent in this principal-agent problem.
C) This is a moral hazard problem.
D) There is no way for Provident to determine whether Susan is a cautious or risky driver.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
An action taken by an informed party to reveal private information to an uninformed party is called
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 441
Related Exams