A) (i) only
B) (ii) only
C) (i) and (ii) only
D) (ii) and (iii) only
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct for both a monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm? (i) The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost. (ii) The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost. (iii) Demand equals marginal revenue. (iv) Average revenue equals price.
A) (i) , (iii) , and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iv) only
C) (i) , (ii) , and (iv) only
D) (i) , (ii) , (iii) , and (iv)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist
A) has a supply curve that is upward-sloping, just like a competitive firm.
B) does not have a supply curve because the monopolist sets its price at the same time it chooses the quantity to supply.
C) has a horizontal supply curve, just like a competitive firm.
D) does not have a supply curve because marginal revenue exceeds the price it charges for its products.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-1
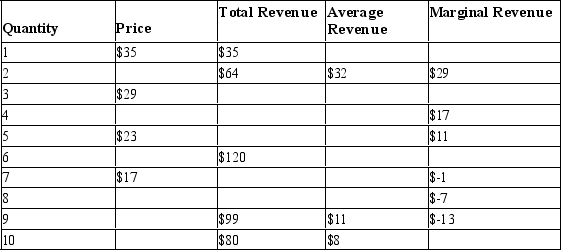 -Refer to Table 15-1. If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue, how many units of its product should it sell?
-Refer to Table 15-1. If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue, how many units of its product should it sell?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 8
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economic inefficiency of a monopolist can be measured by the
A) deadweight loss.
B) value of the unrealized trades that could be made if the monopolist produced the socially-efficient output.
C) area above marginal cost but beneath demand from the monopoly output to the socially-efficient output.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 15-23 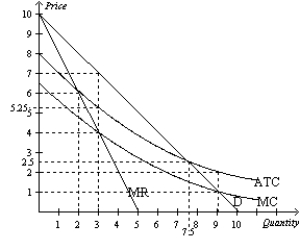 -Refer to Figure 15-23. What type of monopoly is shown in the figure?
-Refer to Figure 15-23. What type of monopoly is shown in the figure?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of price discrimination by a firm?
A) children's meals at a restaurant
B) a natural gas company charging customers a higher rate in the winter than in the summer
C) a senior citizens' discount
D) coupons in the Sunday newspaper
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government regulates the price that a natural monopolist can charge to be equal to the firm's average total cost, the firm will
A) earn zero profits.
B) earn positive profits, causing other firms to enter the industry.
C) earn negative profits, causing the firm to exit the industry.
D) minimize costs in order to lower the price that it charges.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolies use their market power to
A) charge prices that equal minimum average total cost.
B) increase the quantity sold as they increase price.
C) charge a price that is higher than marginal cost.
D) dump excess supplies of their product on the market.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in total surplus between the socially efficient level of production and the monopolist's level of production is
A) offset by regulatory revenues.
B) called a deadweight loss.
C) equal to the monopolist's profit.
D) Both b and c are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to the monopoly outcome with a single price, imperfect price discrimination (i) sometimes raises total surplus. (ii) sometimes lowers total surplus. (iii) always leads to a lower quantity of output.
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) , (ii) , and (iii)
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The socially efficient level of production occurs where the marginal cost curve intersects
A) average variable cost.
B) average total cost.
C) demand.
D) marginal revenue.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-21
Tommy's Tie Company, a monopolist, has the following cost and revenue information. Assume that Tommy's is
able to engage in perfect price discrimination.
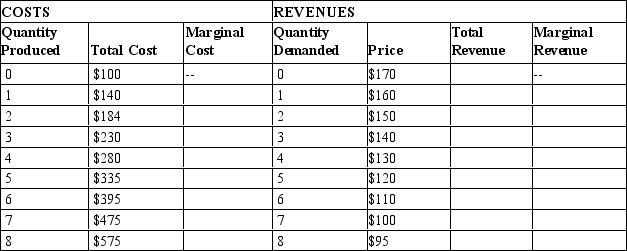 -Refer to Table 15-21. If the monopolist can engage in perfect price discrimination, what is the average revenue when 7 ties are sold?
-Refer to Table 15-21. If the monopolist can engage in perfect price discrimination, what is the average revenue when 7 ties are sold?
A) $90
B) $100
C) $110
D) $130
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-12
The following table provides information on the price, quantity, and average total cost for a monopoly.
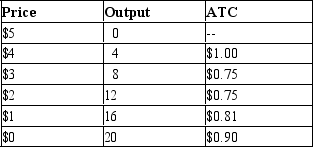 -Refer to Table 15-12. If the firm produces the profit-maximizing level of output, it will earn profits of
-Refer to Table 15-12. If the firm produces the profit-maximizing level of output, it will earn profits of
A) $18.
B) $24.
C) $15.
D) $12.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist that can practice perfect price discrimination will not impose a deadweight loss on society.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Comparing firms in perfectly competitive markets to monopoly firms, which can earn economic profits in the long run?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 15-7 Black Box Cable TV is able to purchase an exclusive right to sell a premium movie channel (PMC) in its market area. Let's assume that Black Box Cable pays $150,000 a year for the exclusive marketing rights to PMC. Since Black Box has already installed cable to all of the homes in its market area, the marginal cost of delivering PMC to subscribers is zero. The manager of Black Box needs to know what price to charge for the PMC service to maximize her profit. Before setting price, she hires an economist to estimate demand for the PMC service. The economist discovers that there are two types of subscribers who value premium movie channels. First are the 4,000 die-hard TV viewers who will pay as much as $150 a year for the new PMC premium channel. Second, the PMC channel will appeal to 20,000 occasional TV viewers who will pay as much as $20 a year for a subscription to PMC. -Refer to Scenario 15-7. What is the deadweight loss associated with the nondiscriminating pricing policy compared to the price discriminating policy?
A) $375,000
B) $400,000
C) $475,000
D) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Drug companies are allowed to be monopolists in the drugs they discover in order to
A) increase the availability of expensive but useful medications.
B) increase the overall welfare of society through better health because drug companies continually produce better medications.
C) encourage research.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 15-8 Mega Media Cable TV is able to purchase an exclusive right to sell a premium sports channel in its market area. Let's assume that Mega Media pays $100,000 a year for the exclusive marketing rights to the sports channel. Since Mega Media has already installed cable to all of the homes in its market area, the marginal cost of delivering the sports channel to subscribers is zero. The manager of Mega Media needs to know what price to charge for the sports channel service to maximize her profit. Before setting price, she hires an economist to estimate demand for the sports channel. The economist discovers that there are two types of subscribers who value premium sporting channels. First are the 3,000 die-hard sports fans who will pay as much as $150 a year for the new channel. Second, the premium sports channel will appeal to 20,000 occasional sports viewers who will pay as much as $25 a year for a subscription to it. -Refer to Scenario 15-8. If Mega Media Cable TV is unable to price discriminate, what price will it choose to maximize its profit, and what is the amount of the profit?
A) price = $25; profit = $575,000
B) price = $25; profit = $475,000
C) price = $150; profit = $450,000
D) price = $150; profit = $350,000
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a reason for the existence of a monopoly?
A) patents
B) marginal-cost pricing
C) economies of scale
D) trademarks
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 637
Related Exams