B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 35-4
Use the graph below to answer the following questions. 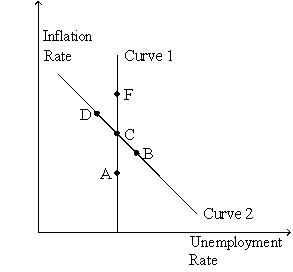 -Refer to Figure 35-4.Curve 2 is the
-Refer to Figure 35-4.Curve 2 is the
A) long-run Phillips curve.
B) short-run Phillips curve.
C) long-run aggregate demand curve.
D) short-run aggregate demand curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samuelson and Solow reasoned that when aggregate demand was low,unemployment was
A) high,so there was upward pressure on wages and prices.
B) high,so there was downward pressure on wages and prices.
C) low,so there was upward pressure on wages and prices.
D) low,so there was downward pressure on wages and prices.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A decrease in the growth rate of the money supply eventually causes the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A favorable supply shock will cause
A) unemployment to rise and the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.
B) unemployment to rise and the short-run Phillips curve to shift left.
C) unemployment to fall and the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.
D) unemployment to fall and the short-run Phillips curve to shift left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 35-5
Use the two graphs in the diagram to answer the following questions. 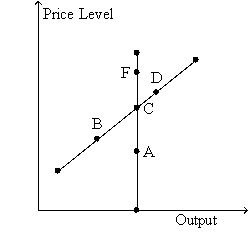
 -Refer to Figure 35-5.Starting from C and 3,in the long run,a decrease in money supply growth moves the economy to
-Refer to Figure 35-5.Starting from C and 3,in the long run,a decrease in money supply growth moves the economy to
A) A and 1.
B) back to C and 3.
C) D and 4.
D) F and 5.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the money supply increases.In the short run,this increases prices according to
A) both the short-run Phillips curve and the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model.
B) neither the short-run Phillips curve nor the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model.
C) the short-run Phillips curve,but not the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model.
D) the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model but not the short-run Phillips curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The large increase in oil prices in the 1970s was caused primarily by a(n)
A) increase in demand for oil.
B) decrease in demand for oil.
C) decrease in the supply of oil.
D) increase in the supply of oil.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A low sacrifice ratio would make a central bank less willing to reduce the inflation rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 35-6
Use this graph to answer the questions below. 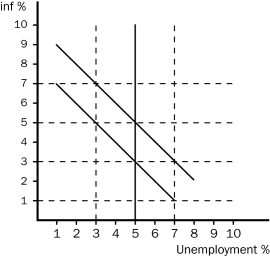 -Refer to figure 35-6.If the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 5% inflation then if the Federal Reserve pursues a contractionary monetary policy,in the short run the economy moves to
-Refer to figure 35-6.If the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 5% inflation then if the Federal Reserve pursues a contractionary monetary policy,in the short run the economy moves to
A) 3% unemployment and 5% inflation.In the long run the economy moves to 5% unemployment and 5% inflation.
B) 3% unemployment and 5% inflation.In the long run the economy moves to 5% unemployment and 3% inflation.
C) 7% unemployment and 3% inflation.In the long run the economy moves to 5% unemployment and 5% inflation.
D) 7% unemployment and 3% inflation.In the long run the economy moves to 5% unemployment and 3% inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure The Economy in 2008 In the first half of June 2008 the effects of a housing and financial crisis and an increase in world prices of oil and foodstuffs were impacting the economy. -Refer to The Economy in 2008.The short-run effects of the housing and financial crisis are shown by
A) moving to the right along the short-run Phillips curve.
B) moving to the left along the short-run Phillips curve.
C) shifting the short-run Phillips curve right.
D) shifting the short-run Phillips curve left.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Friedman and Phelps's analysis of the Phillips curve,
A) the unemployment rate will be below its natural rate whenever inflation is negative.
B) the unemployment rate will be below its natural rate whenever inflation is positive.
C) the unemployment rate will be below its natural rate only if inflation is less than expected.
D) the unemployment rate will be below its natural rate only if inflation is greater than expected.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Moving from the late 1960s to 1970-1973
A) inflation remained high while the unemployment rate was lower than in the late 1960s.
B) inflation remained high while the unemployment rate was higher than in the late 1960s.
C) inflation remained low while the unemployment rate was lower than in the late 1960s.
D) inflation remained low while the unemployment rate was higher than in the late 1960s.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run Phillips curve shows the combinations of
A) unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as aggregate demand shifts the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as short-run aggregate supply shifts the economy along the aggregate demand curve.
C) real GDP and the price level that arise in the short run as short-run aggregate supply shifts the economy along the aggregate demand curve.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From 1993-2001 the U.S.economy experienced
A) relatively low inflation and unemployment rates.
B) relatively high inflation and unemployment rates.
C) relatively low inflation rates and relatively high unemployment rates.
D) relatively high inflation rates and relatively low unemployment rates.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 35-6
Use this graph to answer the questions below.  -Refer to figure 35-6.Suppose the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 3% inflation and expected inflation remains at 3%.Which one of the following points could the economy move to in the short run if the Federal Reserve pursues a more expansionary monetary policy?
-Refer to figure 35-6.Suppose the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 3% inflation and expected inflation remains at 3%.Which one of the following points could the economy move to in the short run if the Federal Reserve pursues a more expansionary monetary policy?
A) 7% unemployment and 1% inflation
B) 7% unemployment and 3% inflation
C) 3% unemployment and 5% inflation
D) 3% unemployment and 7% inflation
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The natural rate of unemployment
A) is constant over time.
B) varies over time,but can't be changed by the government.
C) is the socially desirable rate of unemployment.
D) does not depend on the rate at which the Fed increases the money supply.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his famous article published in an economics journal in 1958,A.W.Phillips
A) used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.S.consumer price index and the U.S.unemployment rate.
B) used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.S.and the U.S.unemployment rate.
C) used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.K.consumer price index and the U.K.unemployment rate.
D) used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.K.and the U.K.unemployment rate.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run an increase in the money supply growth rate effects
A) the inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the inflation rate,but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C) neither the inflation rate nor the natural rate of unemployment.
D) the natural rate of unemployment,but not the inflation rate.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The restrictive monetary policy followed by the Fed in the early 1980s
A) reduced both unemployment and inflation.
B) reduced inflation significantly,but at the cost of a severe recession.
C) reduced unemployment significantly,but at the cost of higher inflation.
D) raised both unemployment and inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 306
Related Exams