A) shift outward relative to the old optimum.
B) move leftward along the old budget constraint.
C) not change.
D) shift inward relative to the old optimum.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic theory predicts that an increase in wages
A) will cause a wage earner to work more.
B) will cause a wage earner to work less.
C) will cause a wage earner to be more productive.
D) might cause a wage earner to work more or work less.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Good X is an inferior good but not a Giffen good.When the price of X increases,the consumer will consume
A) more X.
B) the same amount of X.
C) less X.
D) more or less X depending on the size of the income effect relative to the size of the substitution effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer who doesn't spend all of her income
A) would be at a point outside of her budget constraint.
B) would be at a point inside her budget constraint.
C) must not be consuming positive quantities of all goods.
D) must be consuming at a point where her budget constraint touches one of the axes.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A normal good is one in which
A) the average consumer chooses to consume at a normal level.
B) the average consumer chooses to consume the good over other similar goods.
C) an increase in income increases consumption of the good.
D) an increase in income decreases consumption of the good.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Irene is a vegetarian,so she does not eat pork.That is,pork provides no additional utility to Irene.She loves broccoli,however.If we illustrate Irene's indifference curves by drawing broccoli on the horizontal axis and pork on the vertical axis,her indifference curves will
A) slope downward.
B) be vertical straight lines.
C) slope upward.
D) be horizontal straight lines.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How are the following three questions related: 1) Do all demand curves slope downward? 2) How do wages affect labor supply? 3) How do interest rates affect household saving?
A) They all relate to macroeconomics.
B) They all relate to monetary economics.
C) They all relate to the theory of consumer choice.
D) They are not related to each other in any way.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For a typical consumer,most indifference curves are bowed inward.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If income decreases and prices are unchanged,the consumer's budget constraint
A) remains the same.
B) shifts outward.
C) shifts inward.
D) rotates outward along the horizontal axis.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer has preferences over two goods: books and movies.The two bundles shown in the table below lie on the same indifference curve for the consumer.
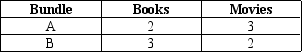 Which of the following bundles could not lie on the same indifference curve with A and B and satisfy the four properties of indifference curves?
Which of the following bundles could not lie on the same indifference curve with A and B and satisfy the four properties of indifference curves?
A) 1 movie and 5 books
B) 3 movies and 3 books
C) 5 movies and 1 book
D) 1 movie and 7 books
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the work-leisure model,suppose consumption and leisure are both normal goods.The income effect of a wage increase results in the worker choosing to
A) work less than before.
B) work more than before.
C) possibly work more or less than before.
D) work more than before with a higher level of consumption.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Giffen goods are inferior goods for which the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The marginal rate of substitution between goods A and B measures the price of A relative to the price of B.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Katie wins $1 million in her state's lottery.If Katie drastically reduces the number of hours she works after she wins the money,we can infer that the income effect is larger than the substitution effect for her.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the budget constraint between "spending today" on the horizontal axis and "spending a year from today" on the vertical axis.Suppose that you have $100 today and expect to receive $100 one year from today.Your money market account pays an annual interest rate of 25%,and you may borrow money at that interest rate.Suppose now that the interest rate decreases to 10%.What happens to the slope of your budget constraint relative to when the interest rate was $25%? The slope
A) becomes steeper.
B) becomes flatter.
C) doesn't change because the budget constraint shifts in parallel to the original budget constraint.
D) doesn't change because the budget constraint shifts out parallel to the original budget constraint.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a property of a typical indifference curve?
A) downward sloping
B) bowed away from the origin
C) do not intersect
D) higher ones are preferred to lower ones
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-2 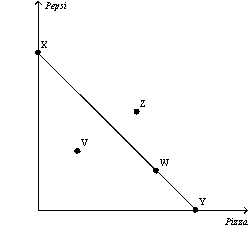 -Refer to Figure 21-2.Which of the following statements is not correct?
-Refer to Figure 21-2.Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Points W,X,and Y all cost the consumer the same amount of money.
B) Point Z is unaffordable for the consumer given his budget constraint.
C) Point V costs less than point Z.
D) Points W,X,and Y give the consumer the same level of satisfaction.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When considering household saving,the relative price between consuming when young and consuming when old is the
A) consumption rate.
B) interest rate that individuals can earn on their private savings.
C) prime rate.
D) federal funds rate.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-7 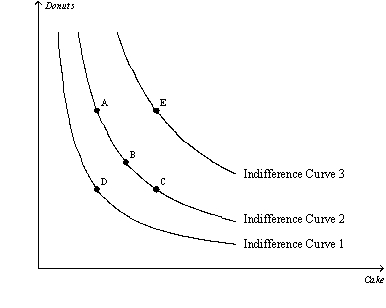 -Refer to Figure 21-7.Which of the following statements is not true for a consumer who moves from bundle B to bundle C?
-Refer to Figure 21-7.Which of the following statements is not true for a consumer who moves from bundle B to bundle C?
A) At bundle C the consumer would be willing to give up a larger amount of cake in exchange for a donut than at bundle B.
B) The marginal rate of substitution at bundles B and C are the same since the points lie on the same indifference curve.
C) The consumer is willing to sacrifice donuts to obtain cake.
D) The consumer receives the same level of satisfaction at bundles B and C.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If consumers purchase more of a good when their income rises,the good is a normal good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 321 - 340 of 354
Related Exams