A) Economics is a study of the choices that people make and the resulting interactions they have with one another.
B) Economists are not interested in finding new areas to study and new phenomena to explain.
C) Economists are trying to expand their understanding of human behavior and society.
D) The economics of asymmetric information, political economy, and behavioral economics are all topics at the frontier of microeconomics.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-4
Suppose that residents of a town are asked to vote on the best way to improve the safety of an intersection. The three choices are: a stoplight, a 4-way stop, and a 2-way stop. The voters are divided into three groups based on their preferences.
Voter Type
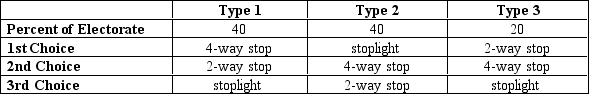 -Refer to Scenario 22-4.Based on the information in the table,which of the following statements is true?
-Refer to Scenario 22-4.Based on the information in the table,which of the following statements is true?
A) In a vote between a 2-way stop and a stoplight, stoplight wins because 40% of voters have stoplight as their 1st choice.
B) In a vote between a 2-way stop and a 4-way stop, the 4-way stop wins getting 80% of the total vote.
C) In a vote between a 4-way stop and a stoplight, there is a tie because each gets 40% of the vote.
D) None of the above are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-3
The citizens of Anytown will decide whether to build a new library, a new community center, or a new ice rink. Exactly one of the three choices will prevail, and the choice will be made by way of pairwise voting, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The preferences of the voters are summarized in the table below.
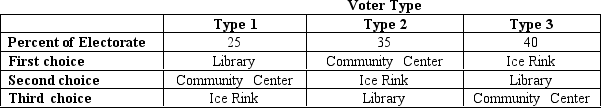 -Refer to Table 22-3.If the citizens of Anytown use an instant runoff election.,then they will build a new
-Refer to Table 22-3.If the citizens of Anytown use an instant runoff election.,then they will build a new
A) library.
B) community center.
C) ice rink.
D) None of the above is correct; an instant runoff fails to produce a winner in this instance.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-4
Five voters must choose from among four options: A, B, C, or D. Each voter's preferences are summarized in the table below. Options higher in the table are more preferred by the voter.
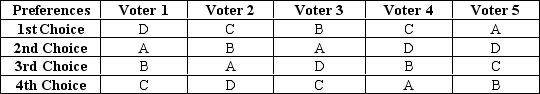 -Refer to Table 22-4.If the vote were conducted according to a modified Borda count system where each person's first choice receives 10 points,second choice 5 points,third choice 3 points and fourth choice 1 point,the result would be that
-Refer to Table 22-4.If the vote were conducted according to a modified Borda count system where each person's first choice receives 10 points,second choice 5 points,third choice 3 points and fourth choice 1 point,the result would be that
A) A would win.
B) B would win.
C) C would win.
D) D would win.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The temptation of imperfectly-monitored workers to shirk their responsibilities is
A) an example of the moral hazard problem.
B) an example of the adverse selection problem.
C) an example of screening.
D) an example of signaling.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Based on studies of human decision making,many people care more about the fairness of a game than about their personal winnings.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-3 Three candidates, Frank, Brian, and Wanda, are running for office. There are three voters in the upcoming election: Henry, Diane, and Linda. Henry prefers Brian over Frank and Frank over Wanda. Diane prefers Wanda over Brian and Brian over Frank. Linda prefers Frank over Brian and Brian over Wanda. -Refer to Scenario 22-3.If the voters were given a choice of Brian versus Wanda first,then the winner was in a second election versus Frank,who would win?
A) Frank
B) Brian
C) Wanda
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scott's Painting Company paints houses.Since Scott's business does not have the name recognition of some of the bigger painting companies,Scott advertises a "Five-Year Money Back Guarantee" to indicate to buyers that his service is of high quality.This guarantee is an example of
A) screening.
B) signaling.
C) the seller's curse.
D) the principal-agent problem.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Manuel buys automobile insurance from Ax-i-Dent Insurance Company.If Manuel avoids having an accident for three years,Ax-i-Dent will reduce the price he has to pay for his insurance.Nevertheless,he routinely drives fast and with reckless abandon.
A) This is an adverse selection problem which should be corrected with government intervention.
B) Manuel is a principal and Ax-i-Dent is an agent in this principal-agent problem.
C) This is a moral hazard problem.
D) There is no way for Ax-i-Dent to determine whether Manuel is a cautious or risky driver.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-7
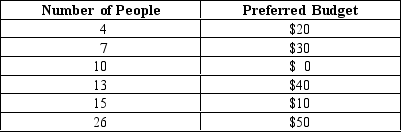 -Refer to Table 22-7.The table shows the most preferred budget of 75 voters.In an election,each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget.Using this information,what is the most preferred budget of the median voter?
-Refer to Table 22-7.The table shows the most preferred budget of 75 voters.In an election,each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget.Using this information,what is the most preferred budget of the median voter?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $40
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your friend works at a coffee shop on campus and regularly gives away free coffee to you and your friends when you visit.If the owner of the coffee shop wants to stop your friend from giving away coffee,which of the following is not a good approach?
A) Set up a video camera to monitor the shop when the owner is not present.
B) Pay your friend a wage higher than he could earn elsewhere for the same position.
C) Pay your friend in advance based on projected revenue each month.
D) Pay your friend part of his compensation as a monthly bonus based on revenue.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The buyer runs a risk of being sold a good of low quality when there is
A) a principal-agent problem.
B) a moral-hazard problem.
C) a problem involving hidden actions.
D) a problem involving hidden characteristics.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mankiw argues that a primary difference between taxing products like gasoline and taxing soda and other sugary drinks is that
A) consumption of gasoline causes negative externalities on society while consumption of soda affects the consumer.
B) the government can generate significant revenue from the gas tax but not from a soda tax.
C) gasoline has inelastic demand but soda has elastic demand.
D) Both a and c are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Borda count fails to satisfy which of Kenneth Arrow's properties of a "perfect" voting system?
A) no dictator
B) unanimity
C) transitivity
D) independence of irrelevant alternatives
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Studies show that during the March Madness college basketball tournament,the productivity of average company in the US falls considerably.This is an example of
A) the Condorcet Paradox.
B) signaling.
C) moral hazard.
D) screening.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-14
The Johnson family is planning a vacation and, though Mr. and Mrs. Johnson will be paying for the trip, they have decided to use a democratic voting process to choose their destination. The family members' preferences are reflected in the table below.
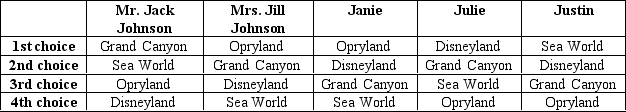 -Refer to Table 22-14.Mr.Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule.If he wants to ensure that his 1st choice becomes the family's winning destination,he should propose
-Refer to Table 22-14.Mr.Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule.If he wants to ensure that his 1st choice becomes the family's winning destination,he should propose
A) first choosing between Opryland and the Grand Canyon, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Sea World, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Disneyland.
B) first choosing between Disneyland and Sea World, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and the Grand Canyon and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and the Opryland.
C) first choosing between Sea World and the Grand Canyon, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Disneyland, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Opryland.
D) first choosing between Opryland and Disneyland, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and the Grand Canyon, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Sea World.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-1
Three friends -- Tricia, Sarah, and Katie -- are deciding where to go together for vacation. They all agree that they should go to one of three places: Ireland, Italy, or Greece. They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine where to go on vacation, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.
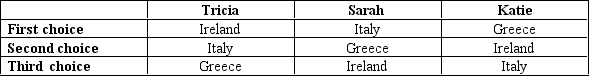 -Refer to Table 22-1.Depending on the order of the pairwise voting,
-Refer to Table 22-1.Depending on the order of the pairwise voting,
A) the friends could go to either Ireland, Greece, or Italy.
B) the friends could go to either Ireland or Greece, but they will not go to Italy.
C) the friends could go to either Greece or Italy, but they will not go to Ireland.
D) the friends could go to either Ireland or Italy, but they will not go to Greece.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Condorcet paradox tells us that,even though it is impossible to satisfy all of Arrow's properties of a desirable voting system,pairwise majority voting will always satisfy transitivity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-3
The citizens of Anytown will decide whether to build a new library, a new community center, or a new ice rink. Exactly one of the three choices will prevail, and the choice will be made by way of pairwise voting, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The preferences of the voters are summarized in the table below.
 -Refer to Table 22-3.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting in Anytown?
-Refer to Table 22-3.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting in Anytown?
A) The paradox implies that pairwise voting never produces transitive preferences, and so the voting in Anytown fails to produce transitive preferences.
B) The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) produces transitive preferences, and the voting in Anytown does produce transitive preferences.
C) The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) fails to produce transitive preferences, and the voting in Anytown fails to produce transitive preferences.
D) The paradox does not apply to the case at hand, because the preferences of Type 3 voters are not individually transitive.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which voter is the voter whose views on a policy issue are in the middle of the spectrum,with half of the voters on one side of this voter's view and half on the other side.
A) Average voter
B) Mean voter
C) Modal voter
D) Median voter
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 281 - 300 of 353
Related Exams