A) the gains of the domestic producers of the good exceed the losses of the domestic consumers of the good.
B) the gains of the domestic consumers of the good exceed the losses of the domestic producers of the good.
C) the losses of the domestic producers of the good exceed the gains of the domestic consumers of the good.
D) the losses of the domestic consumers of the good exceed the gains of the domestic producers of the good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-6
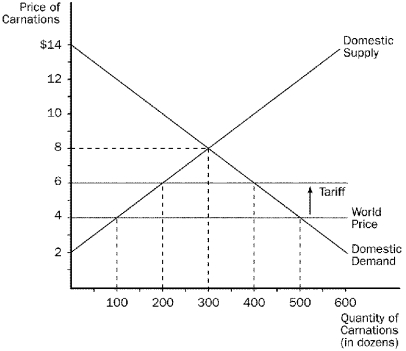 -Refer to Figure 9-6.Before the tariff is imposed,this country
-Refer to Figure 9-6.Before the tariff is imposed,this country
A) imports 200 carnations.
B) imports 400 carnations.
C) exports 200 carnations.
D) exports 400 carnations.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By comparing the world price of horseradish to Cropland's domestic price of horseradish,we can determine whether Cropland
A) will export horseradish (assuming trade is allowed) .
B) will import horseradish (assuming trade is allowed) .
C) has a comparative advantage in producing horseradish.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-1
The figure illustrates the market for wool in Scotland.
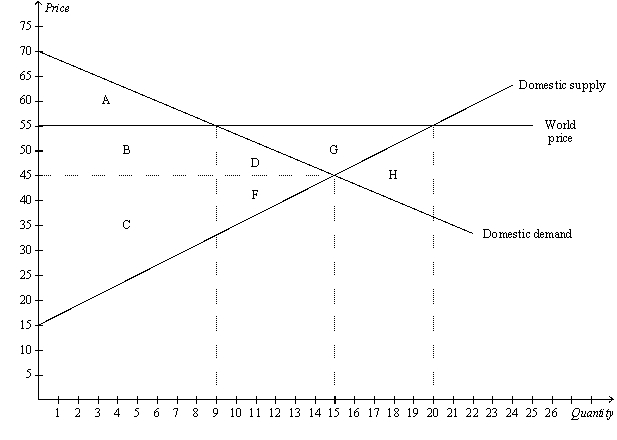 -Refer to Figure 9-1.When trade is allowed,
-Refer to Figure 9-1.When trade is allowed,
A) Scotland producers of wool become better off and Scotland consumers of wool become worse off.
B) Scotland consumers of wool become better off and Scotland producers of wool become worse off.
C) both Scotland producers and consumers of wool become better off.
D) both Scotland producers and consumers of wool become worse off.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a country abandons a no-trade policy,adopts a free-trade policy,and becomes an exporter of a particular good,
A) consumer surplus increases and total surplus increases in the market for that good.
B) consumer surplus increases and total surplus decreases in the market for that good.
C) consumer surplus decreases and total surplus increases in the market for that good.
D) consumer surplus decreases and total surplus decreases in the market for that good.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-1
The figure illustrates the market for wool in Scotland.
 -Refer to Figure 9-1.With trade,total surplus in the Scotland wool market amounts to
-Refer to Figure 9-1.With trade,total surplus in the Scotland wool market amounts to
A) 312.5.
B) 367.0.
C) 467.5.
D) 495.0.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-17
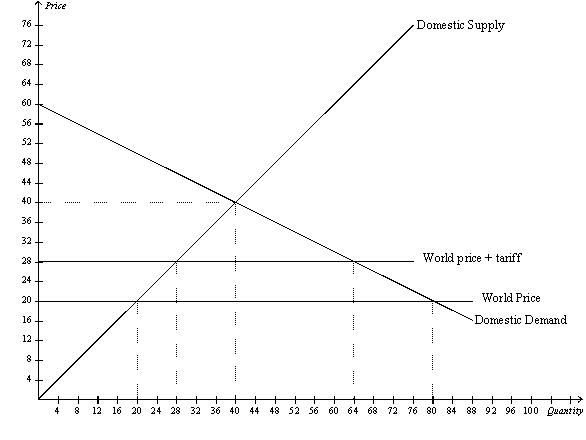 -Refer to Figure 9-17.The deadweight loss caused by the tariff is
-Refer to Figure 9-17.The deadweight loss caused by the tariff is
A) $24.
B) $72.
C) $96.
D) $144.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The problem with the protection-as-a-bargaining-chip argument for trade restrictions is
A) if it works consumer surplus will decline.
B) if it works producer surplus falls.
C) if it fails the country faces a choice between two bad options.
D) if it fails total surplus will increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-15
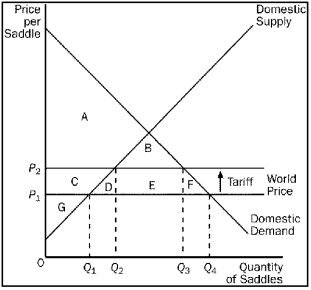 -Refer to Figure 9-15.Producer surplus with trade and without a tariff is
-Refer to Figure 9-15.Producer surplus with trade and without a tariff is
A) G.
B) C + G.
C) A + C + G.
D) A + B + C + G.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-1
The figure illustrates the market for wool in Scotland.
 -Refer to Figure 9-1.From the figure it is apparent that
-Refer to Figure 9-1.From the figure it is apparent that
A) Scotland will experience a shortage of wool if trade is not allowed.
B) Scotland will experience a surplus of wool if trade is not allowed.
C) Scotland has a comparative advantage in producing wool, relative to the rest of the world.
D) foreign countries have a comparative advantage in producing wool, relative to Scotland.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-12
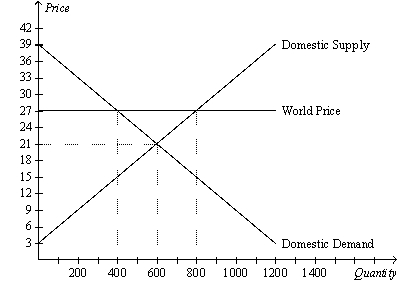 -Refer to Figure 9-12.Producer surplus after trade is
-Refer to Figure 9-12.Producer surplus after trade is
A) $7,000.
B) $7,500.
C) $8,800.
D) $9,600.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the nation of Duxembourg allows trade and becomes an importer of software,
A) residents of Duxembourg who produce software become worse off; residents of Duxembourg who buy software become better off; and the economic well-being of Duxembourg rises.
B) residents of Duxembourg who produce software become worse off; residents of Duxembourg who buy software become better off; and the economic well-being of Duxembourg falls.
C) residents of Duxembourg who produce software become better off; residents of Duxembourg who buy software become worse off; and the economic well-being of Duxembourg rises.
D) residents of Duxembourg who produce software become better off; residents of Duxembourg who buy software become worse off; and the economic well-being of Duxembourg falls.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a country that exported a particular good abandons a free-trade policy and adopts a no-trade policy,
A) consumer surplus increases and total surplus increases in the market for that good.
B) consumer surplus increases and total surplus decreases in the market for that good.
C) consumer surplus decreases and total surplus increases in the market for that good.
D) consumer surplus decreases and total surplus decreases in the market for that good.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
William and Jamal live in the country of Dumexia.When Dumexia legalized international trade in bananas,the price of bananas in Dumexia increased.As a result,William became better off and Jamal became worse off.It follows that William is a seller,and Jamal is a buyer,of bananas.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a country allows trade and becomes an importer of a good,
A) everyone in the country benefits.
B) the gains of the winners exceed the losses of the losers.
C) the losses of the losers exceed the gains of the winners.
D) everyone in the country loses.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Freedonia changes its laws to allow international trade in software and the world price is lower than its domestic price,then it must be the case that
A) both consumer surplus and producer surplus increase.
B) consumer surplus increases and producer surplus decreases.
C) consumer surplus decreases and producer surplus increases.
D) both consumer surplus and producer surplus decrease.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a country allows trade and becomes an importer of a good,
A) both domestic producers and domestic consumers become better off.
B) domestic producers become better off, and domestic consumers become worse off.
C) domestic producers become worse off, and domestic consumers become better off.
D) both domestic producers and domestic consumers become worse off.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-20
The figure illustrates the market for rice in Vietnam.
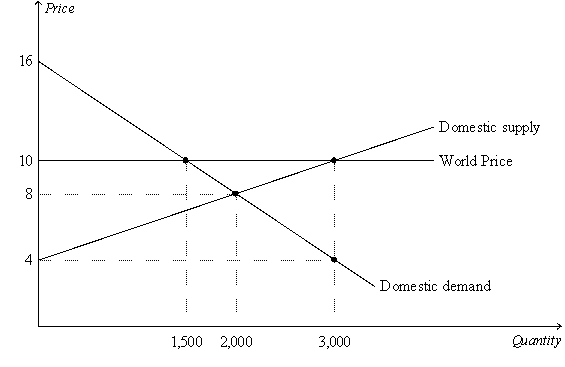 -Refer to Figure 9-20.With trade,Vietnamese rice producers will produce
-Refer to Figure 9-20.With trade,Vietnamese rice producers will produce
A) 2,000 units of rice and their producer surplus will be 4,000.
B) 2,000 units of rice and their producer surplus will be 7,500.
C) 3,000 units of rice and their producer surplus will be 7,500.
D) 3,000 units of rice and their producer surplus will be 9,000.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major difference between tariffs and import quotas is that
A) tariffs create deadweight losses, but import quotas do not.
B) tariffs help domestic consumers, and import quotas help domestic producers.
C) tariffs raise revenue for the government, but import quotas create surplus for those who get the licenses to import.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-7. The figure applies to the nation of Wales and the good is cheese.
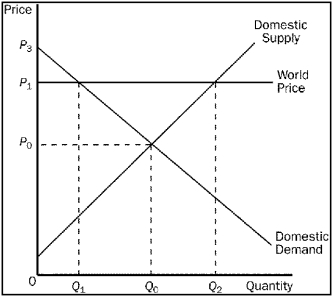 -Refer to Figure 9-7.With trade,Wales
-Refer to Figure 9-7.With trade,Wales
A) imports Q2 - Q1 units of cheese.
B) exports Q2 - Q1 units of cheese.
C) imports Q2 - Q0 units of cheese.
D) exports Q2 - Q0 units of cheese.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 410
Related Exams