A) unwillingness to give up a good that he already has in large quantity.
B) unwillingness to purchase a good that he already has in large quantity.
C) greater willingness to give up a good that he already has in large quantity.
D) greater willingness to purchase a good that he already has in large quantity.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of consumer choice
A) underlies the concept of the demand for a particular good.
B) underlies the concept of the supply of a particular good.
C) ignores, for the sake of simplicity, the trade-offs that consumers face.
D) can be applied to many questions about household decisions, but it cannot be applied to questions concerning wages and labor supply.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A budget constraint shows
A) the maximum utility that a consumer can achieve for a given level of income.
B) a series of bundles that cost the consumer the same amount of money.
C) a series of bundles that give the consumer the same level of utility.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the work-leisure model, suppose consumption and leisure are both normal goods. The income effect of a wage increase results in the worker choosing to
A) work less than before.
B) work more than before.
C) possibly work more or less than before.
D) work more with a higher level of consumption.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Suzette responds to an increase in the interest rate by decreasing her saving, then, for Suzette,
A) the increase in the interest rate creates an income effect that is greater than the substitution effect.
B) the increase in the interest rate creates a substitution effect that is greater than the income effect.
C) consumption when young and consumption when old are perfect substitutes.
D) consumption when young and consumption when old are perfect complements.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 21-3 Scott knows that he will ultimately face retirement. Assume that Scott will experience two periods in his life, one in which he works and earns income, and one in which he is retired and earns no income. Scott can earn $250,000 during his working period and nothing in his retirement period. He must both save and consume in his work period with an interest rate of 10 percent on savings. -Refer to Scenario 21-3. Assume that Scott decides to consume $100,000 in the work period. How much money will he have available for consumption in his retirement period?
A) $100,000
B) $110,000
C) $150,000
D) $165,000
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that a college student spends her income on mac-n-cheese and CDs. The price of one box of mac-n-cheese is $1, and the price of one CD is $12. If she has $200 of income, she could choose to consume
A) 30 boxes of mac-n-cheese and 12 CDs.
B) 40 boxes of mac-n-cheese and 14 CDs.
C) 20 boxes of mac-n-cheese and 16 CDs.
D) 60 boxes of mac-n-cheese and 12 CDs.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) An increase in income shifts a consumer's budget constraint outward.
B) An increase in the price of good X causes a consumer's budget constraint to rotate inward along the X axis.
C) A decrease in the price of good Y causes a consumer's budget constraint to rotate outward along the Y axis.
D) Changes in income affect the slope of the budget constraint as well as its location on a graph.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-25 The figure pertains to a particular consumer. On the axes, X represents the quantity of good X and Y represents the quantity of good Y. 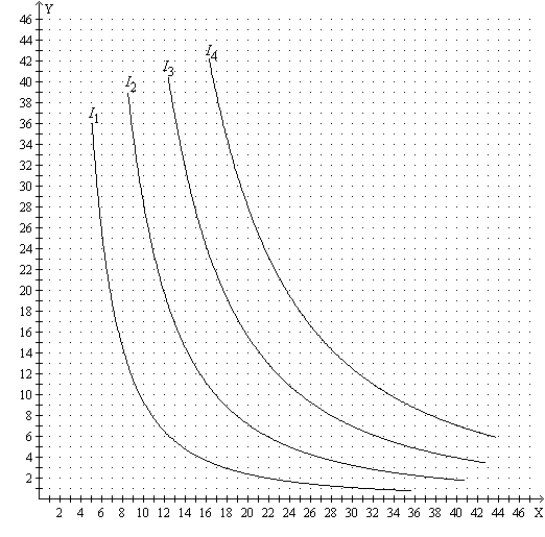 -Refer to Figure 21-25. Suppose the price of good X is $15, the price of good Y is $10, and the consumer's income is $450. Then the consumer's optimal choice is represented by a point on which curve?
-Refer to Figure 21-25. Suppose the price of good X is $15, the price of good Y is $10, and the consumer's income is $450. Then the consumer's optimal choice is represented by a point on which curve?
A) I1
B) I2
C) I3
D) I4
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer likes two goods: hamburgers and watermelons. The five bundles shown in the table below lie on the same indifference curve for the consumer.
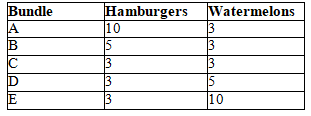 Which of the following statements regarding these bundles is correct?
Which of the following statements regarding these bundles is correct?
A) The goods are perfect substitutes for this consumer.
B) The goods are perfect complements for this consumer.
C) The bundles violate the property that indifference curves do not cross.
D) Both b) and c) are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the interest rate rises, an individual could choose to
A) increase consumption when young.
B) increase consumption when old.
C) decrease consumption when young.
D) Any of the above could be correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the upward-sloping portion of the individual labor-supply curve, the substitution effect is
A) greater than the income effect.
B) less than the income effect.
C) equal to the income effect.
D) exactly offset by the income effect.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists describe preferences, they often use the concept of
A) markets.
B) income.
C) utility.
D) prices.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a consumer is purchasing the best combination of two goods, X and Y, subject to a budget constraint, we say that the consumer is at an optimal choice point. A graph of an optimal choice point shows that it occurs
A) along the highest attainable indifference curve.
B) where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint.
C) where the marginal utility per dollar spent is the same for both X and Y.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer is currently spending all of her available income on two goods: music CDs and DVDs. At her current consumption bundle, she is spending twice as much on CDs as she is on DVDs. If the consumer has $120 of income and is consuming 10 CDs and 2 DVDs, what is the price of a CD?
A) $4
B) $8
C) $12
D) $20
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of an inferior good increases,
A) both the income and substitution effects encourage the consumer to purchase more of the good.
B) both the income and substitution effects encourage the consumer to purchase less of the good.
C) the income effect encourages the consumer to purchase more of the good, and the substitution effect encourages the consumer to purchase less of the good.
D) the income effect encourages the consumer to purchase less of the good, and the substitution effect encourages the consumer to purchase more of the good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations corresponds to an optimal choice point? (i) MRS = PX/PY (ii) MUX/MUY = PX/PY (iii) MUX/PX = MUY/PY (iv) MUX/PY = MUY/PX
A) (i) only
B) (i) , (ii) , and (iii) only
C) (ii) and (iv) only
D) (i) , (ii) , (iii) , and (iv)
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that Milton likes to consume one glass of milk with every three chocolate chip cookies. For Milton, an additional cookie has no value unless he can consume it with the appropriate proportion of milk. Milton's indifference curves for milk and cookies are
A) right angles.
B) bowed inward.
C) bowed outward.
D) downward-sloping straight lines.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When indifference curves are bowed inward, the marginal rate of substitution varies at each point on the indifference curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-20
The following graph illustrates a representative consumer's preferences for marshmallows and chocolate chip cookies: 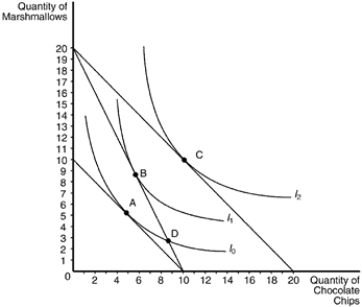 -Refer to Figure 21-20. Assume that the consumer has an income of $40. Based on the information available in the graph, which of the following price-quantity combinations would be on her demand curve for marshmallows if the price of chocolate chips were $4?
-Refer to Figure 21-20. Assume that the consumer has an income of $40. Based on the information available in the graph, which of the following price-quantity combinations would be on her demand curve for marshmallows if the price of chocolate chips were $4?
A) P=$2, Q=3
B) P=$2, Q=9
C) P=$4, Q=3
D) P=$4, Q=9
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 521 - 540 of 570
Related Exams