A) along the highest indifference curve.
B) along the lowest budget constraint.
C) where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer's preferences for right shoes and left shoes can be represented by indifference curves that are
A) bowed out from the origin
B) bowed in toward the origin
C) straight lines
D) right angles
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of the budget constraint is determined by the
A) relative price of the goods measured on the axes.
B) relative price of the goods measured on the axes and the consumer's income.
C) endowment of productive resources.
D) preferences of the consumer.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-6 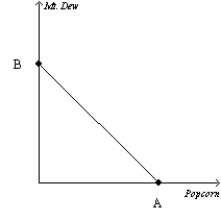 -Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose a consumer has $200 in income, the price of popcorn is $1, and the price of Mt. Dew is $2. What is the value of A?
-Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose a consumer has $200 in income, the price of popcorn is $1, and the price of Mt. Dew is $2. What is the value of A?
A) 200
B) 100
C) 50
D) 25
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the budget constraint between "spending today" on the horizontal axis and "spending a year from today" on the vertical axis. Suppose that you have $100 today and expect to receive $100 one year from today. Your money market account pays an annual interest rate of 25%, and you may borrow money at that interest rate. Suppose now that the interest rate increases to 40%. What happens to the slope of your budget constraint relative to when the interest rate was 25%? The slope
A) becomes steeper.
B) becomes flatter.
C) doesn't change because the budget constraint shifts in parallel to the original budget constraint.
D) doesn't change because the budget constraint shifts out parallel to the original budget constraint.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-5
(a)
(b) 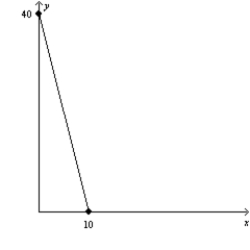
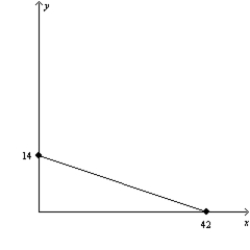 -Refer to Figure 21-5. Assume that a consumer faces the budget constraint shown in graph (a) in January and the budget constraint shown in graph (b) in February. If the consumer's income has remained constant, then what has happened to prices between January and February?
-Refer to Figure 21-5. Assume that a consumer faces the budget constraint shown in graph (a) in January and the budget constraint shown in graph (b) in February. If the consumer's income has remained constant, then what has happened to prices between January and February?
A) The price of X has fallen, but there could not have been a change in the price of Y.
B) The price of Y has fallen, but there could not have been a change in the price of X.
C) The price of X has fallen, and the price of Y has risen.
D) The price of Y has fallen, and the price of X has risen.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-16 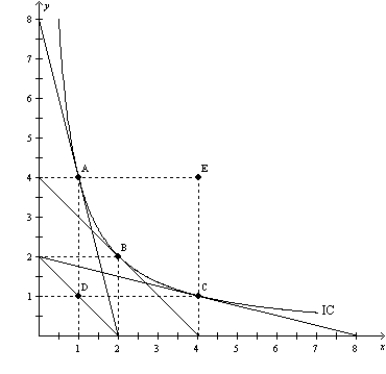 -Refer to Figure 21-16. The price of X is $25, the price of Y is $25, and the consumer's income is $100. Which point represents the consumer's optimal choice?
-Refer to Figure 21-16. The price of X is $25, the price of Y is $25, and the consumer's income is $100. Which point represents the consumer's optimal choice?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a consumer consumes two goods, X and Y, and has indifference curves that are bowed inward, the consumer's optional choice occurs when
A) he consumes the maximum affordable quantity of good X.
B) he consumes the maximum affordable quantity of good Y.
C) his indifference curve is tangent to his budget constraint.
D) his indifference curve lies entirely above his budget constraint.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
At a consumer's optimal choice, the consumer chooses the combination of goods such that the ratio of the marginal utilities equals the ratio of the prices.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution
A) varies along an indifference curve if the curve is bowed inward.
B) is constant along an indifference curve if the curve is a straight line.
C) is greater when a consumer has more of two goods rather than less of two goods.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which effect of a price change moves the consumer along the same indifference curve to a point with a new marginal rate of substitution?
A) the budget effect
B) the preference effect
C) the substitution effect
D) the income effect
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer likes two goods: books and movies. The two bundles shown in the table below lie on the same indifference curve for the consumer.
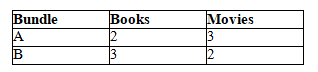 Which of the following bundles could not lie on the same indifference curve with A and B and satisfy the four properties of indifference curves?
Which of the following bundles could not lie on the same indifference curve with A and B and satisfy the four properties of indifference curves?
A) 1 movie and 5 books
B) 3 movies and 3 books
C) 5 movies and 1 book
D) 1 movie and 7 books
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in a consumer's income
A) increases the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
B) has no effect on the consumer's budget constraint.
C) decreases the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
D) has no effect on the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the interest rate today leading to a decrease in consumption today violates the law of demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-18 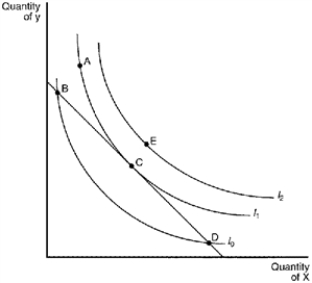 -Refer to Figure 21-18. Given the budget constraint depicted in the graph, the consumer's optimal choice will be point
-Refer to Figure 21-18. Given the budget constraint depicted in the graph, the consumer's optimal choice will be point
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the relative price of a concert ticket is three times the price of a meal at a good restaurant, then the opportunity cost of a concert ticket can be measured by the
A) slope of the budget constraint.
B) slope of an indifference curve.
C) marginal rate of substitution.
D) income effect.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-23 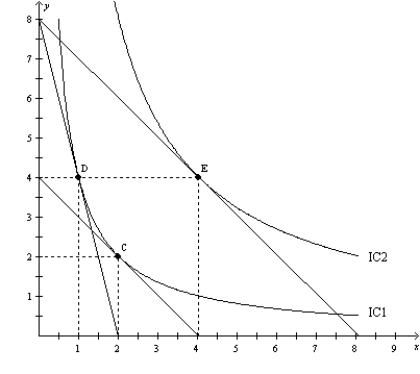 -Refer to Figure 21-23. When the price of X is $80, the price of Y is $20, and the consumer's income is $160, the consumer's optimal choice is D. Then the price of X decreases to $20. The income effect can be illustrated as the movement from
-Refer to Figure 21-23. When the price of X is $80, the price of Y is $20, and the consumer's income is $160, the consumer's optimal choice is D. Then the price of X decreases to $20. The income effect can be illustrated as the movement from
A) D to E.
B) D to C.
C) C to E.
D) E to D.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-25 The figure pertains to a particular consumer. On the axes, X represents the quantity of good X and Y represents the quantity of good Y. 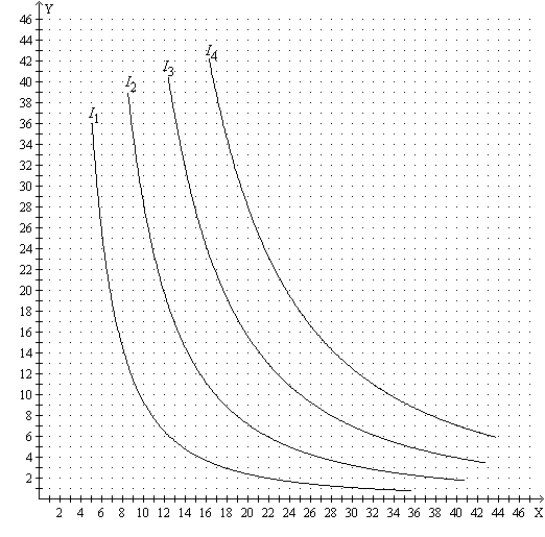 -Refer to Figure 21-25. Suppose the price of good X is $8, the price of good Y is $10, and the consumer's income is $360. Then the consumer's optimal choice is to buy
-Refer to Figure 21-25. Suppose the price of good X is $8, the price of good Y is $10, and the consumer's income is $360. Then the consumer's optimal choice is to buy
A) 15 units of good X and 24 units of good Y.
B) 20 units of good X and 20 units of good Y.
C) 30 units of good X and 12 units of good Y.
D) 40 units of good X and 4 units of good Y.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jack and Diane each buy pizza and paperback novels. Pizza costs $3 per slice, and paperback novels cost $5 each. Jack has a budget of $30, and Diane has a budget of $15 to spend on pizza and paperback novels. Which consumer(s) can afford to purchase 5 slices of pizza and 3 paperback novels?
A) Jack only
B) Diane only
C) both Jack and Diane
D) neither Jack nor Diane
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect complements, the indifference curve is
A) a horizontal straight line.
B) bowed outward.
C) a downward-sloping straight line.
D) a right angle.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 501 - 520 of 570
Related Exams